"A person takes a few steps forward, jumps forward with both feet , and immediately turns right upon landing"
Abstract
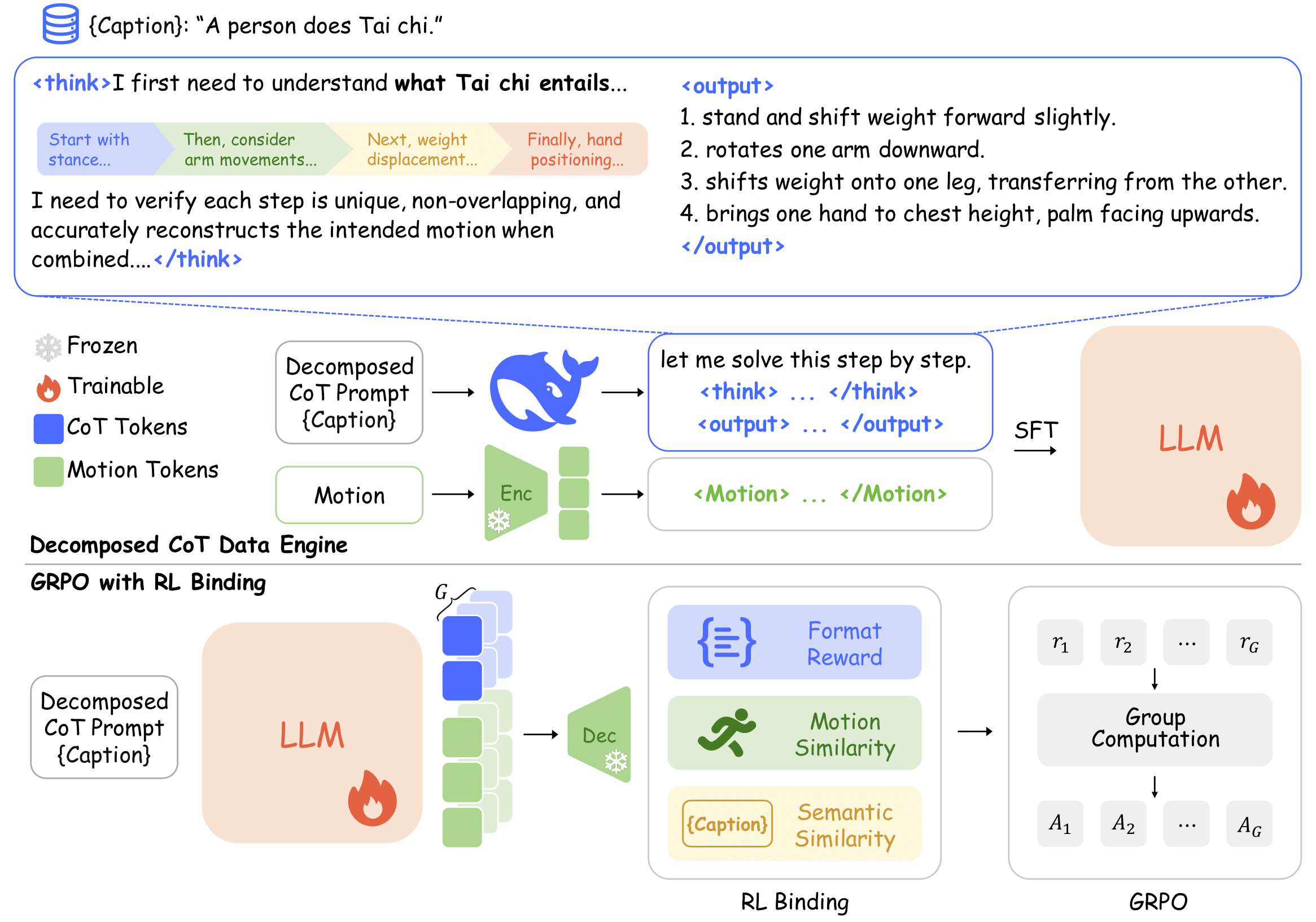
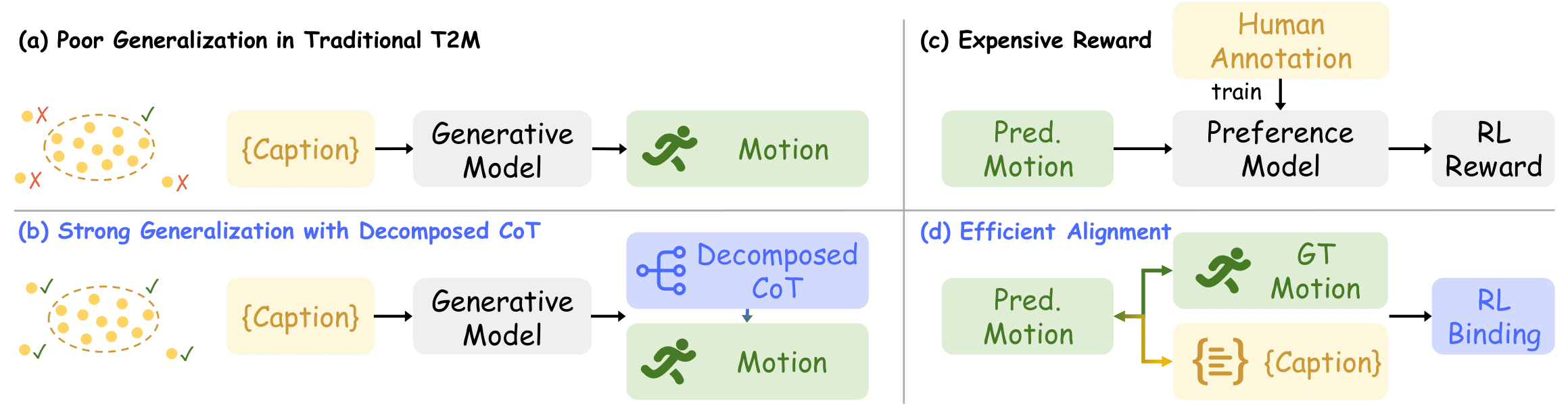
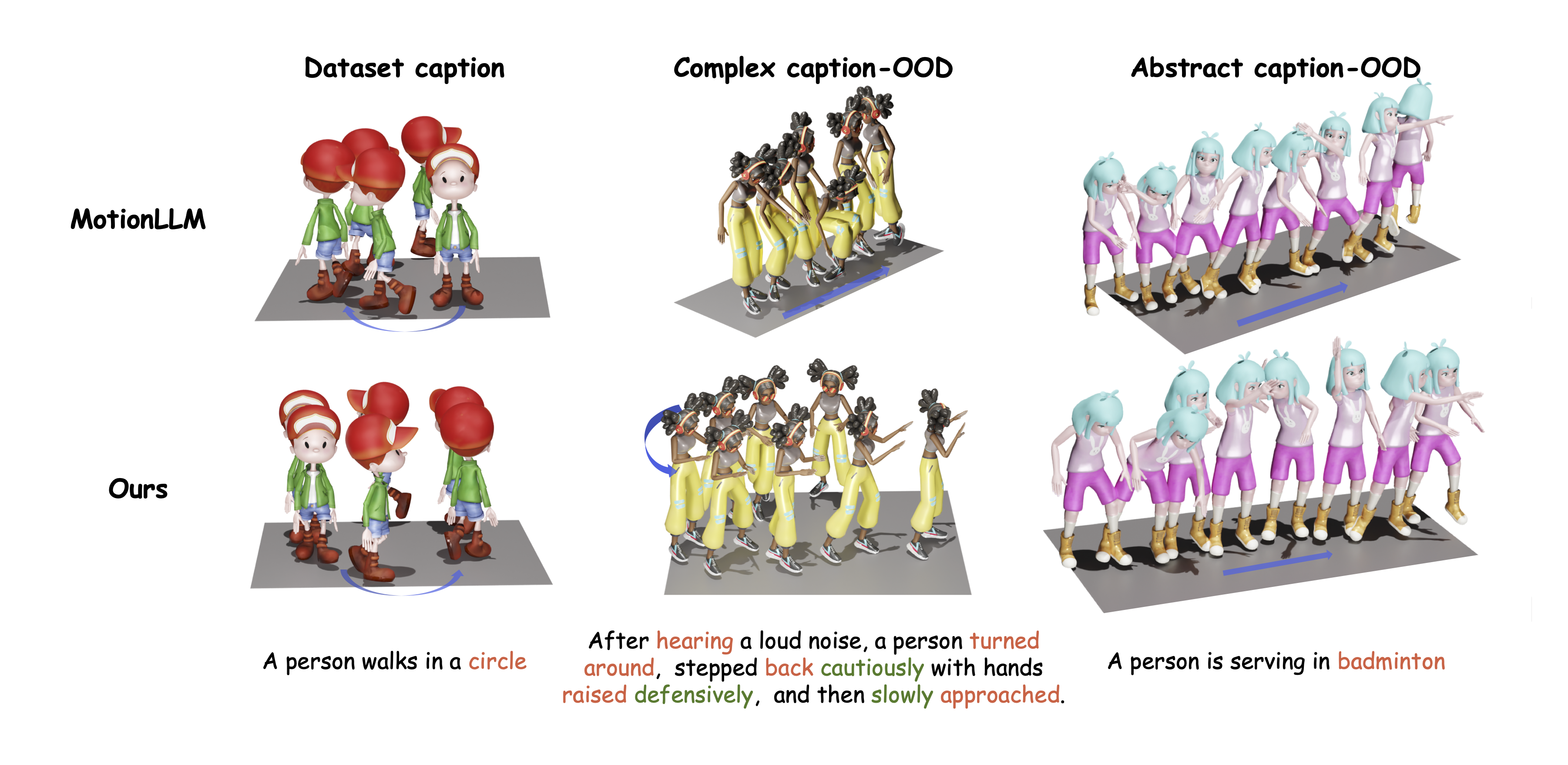
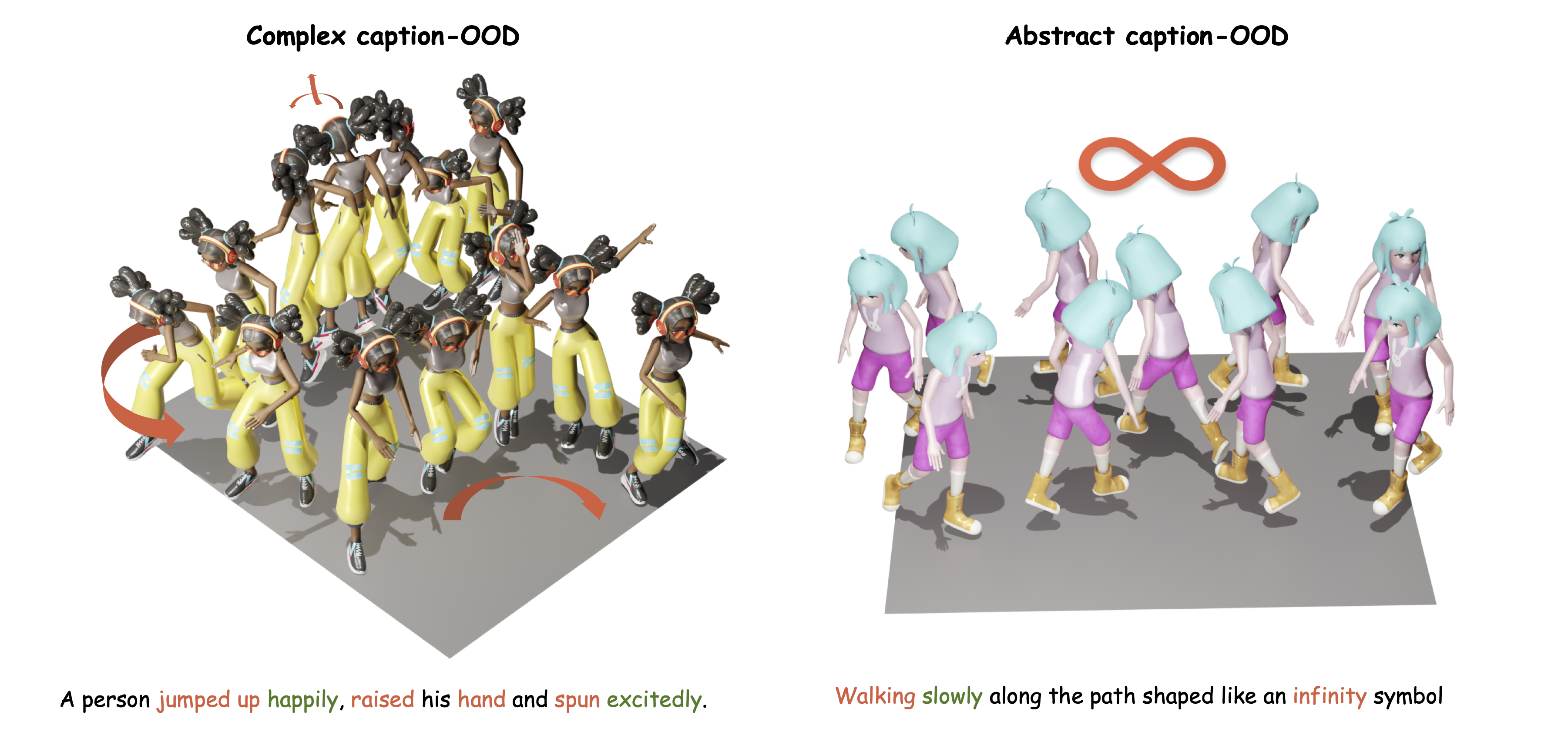
Text-to-Motion generation has become a fundamental task in human-machine interaction, enabling the synthesis of realistic human motions from natural language descriptions. Although recent advances in large language models and reinforcement learning have contributed to high-quality motion generation, two major challenges remain. Existing approaches often fail to capture the temporal and causal complexities inherent in natural language, leading to oversimplified or incoherent motions. Additionally, RL-based methods are frequently overly complex, hindering their scalability and adaptability across various motion generation tasks. To address these challenges, we propose Motion-R1, a novel framework that combines decomposed Chain-of-Thought reasoning with reinforcement learning to enhance both the quality and interpretability of generated motions. Specifically, we introduce the Decomposed CoT Data Engine, which leverages an automated pipeline to synthesize high-quality reasoning data, allowing the model to better capture the temporal dependencies and causal relationships of human motion. We also propose RL Binding, a reinforcement learning strategy that incorporates multi-modal text-motion alignment into the RL reward function, guiding the model to produce motions that are both semantically accurate and motionally realistic. Extensive experiments across benchmark datasets demonstrate that Motion-R1 achieves state-of-the-art performance, with a 3.5% improvement in MM-Dist on HumanML3D and improvements in R-Precision and FID on KIT-ML and BABEL, surpassing existing methods across key metrics and highlighting its superior capability in handling complex motion generation tasks.